By looking at the balance sheet of
the company one can understand how the company has build wealth for itself and
its owners over the past years.
Balance sheet of a company makes one
thing clear about the business, it talks about from where the company is
generating funds to run its business, and where the company is using those
funds.
Any company generate funds in three
possible ways. It can borrow money from stock market. This is called share
capital in balance sheet.
The company can also retain its net
profits to run the business. This is called reserves and surplus in the
balance sheet.
Company can also borrow funds from
Bank etc. This is recorded as long term borrowing and short term borrowing in
balance sheet.
Hence, the total funds available
with a company to run its business can be summed up like this:
Total Funds = Share Capital +
Reserves + Debt.
{Note: Share Capital + Reserves =
Book Value.}
This (total funds) is also called
the total liability of the company.
How the company uses their generated
funds is also indicated in the balance sheet.
Company use its generated funds to
build assets. These assets intern generate income for the company.
Let’s see the important constituents
of a balance sheet in more detail.
Balance sheet basically defines this
equation:
If one read a balance sheet statement
of a company, it will show how much accumulated wealth the company has amassed
till that day.
Shareholders
fund (Book Value / Net Worth)
Why it is called as shareholders
fund?
Shareholders fund is that money that
companies owe to their shareholders.
Shareholders have a legal claim on
the company’s net profits. Hence any funds that is retained by the company
(Reserves) goes into the account of shareholders funds.
Company consider these funds as that
money which they need to pay-back to the shareholders one day.
Book Value = Share Capital +
Reserves
Share capital: is that money that the company has generated from its IPO.
Share capital is actually the
borrowed money that the company has taken from the shareholders.
It is also treated as companies
liability.
Reserves :are also referred as retained net profits of the company.
Why companies retain their profits?
This is done to strengthen their balance sheet (financial position).
Companies used a reserves to buy new
fixed assets. This day 2 by means of capital expenditure plans (CAPEX).
Companies also use their reserves to
reduce there debt burden.
A portion of reserves is also used
to pay dividends to its existing shareholders.
General there are two types of
reserves. First, revenue reserve and second, is called capital Reserves.
Revenue reserves is again
categorized into two types, first he is general reserves and second is specific
reserves.
As the name suggests, general
reserves is not apportioned for any specific purpose. They are just kept in
the balance sheet to strengthen the financial position of the company.
Specific reserves are those portion of money which is kept for specific
purpose. The the funds kept in the specific reserve shall be used only for the
designated purpose.
How the reserves in the balance
sheet is funded every year?
The annual profits of the company
that is shown as net profit, in profit and loss account, is transferred to the
company’s balance sheet as retained earnings.
This retained earning in turn is
used as the reserves of the company.
If the company has made a loss in a
particular financial year, no transaction is recorded in the reserves column of
the balance sheet.
Sometimes, in case of loss, the
company may even debit there reserves account in balance sheet to meet their
requirements.
In such case one will find a dip in
the reserves and surplus account as compared to the previous year.
One of the most important financial
indicator detailed in the Balance Sheet is shareholders equity. In doing a
balance sheet analysis it plays an important role.
Net worth of a company is equal to
total capital generated by the company by issuing stocks and accumulated
retained earnings.
A continuously improving net worth
is what investors likes to see in companies balance sheet.
Investors must compare last five
years net worth of the company, and must also check growth rate.
It is important to check how the net
worth of company has grown.
If increase in net worth is
attributable only to the issuance of more stocks to public, then it is not
good.
Ideally, the companies net worth
must increase due to growth in retained earnings.
Liability
Non current liabilities
Non current liabilities are those
liabilities of a company which is settled only after 12 months from the date of
reporting.
These are such liabilities that
company need not settle immediately.
If you will see in moneycontrol.com,
you will find that non current liabilities are mainly recorded in two three
some heads. First he’s long term borrowing. Second, is deferred tax liability
and third is long term provisions.
Companies which show the line item
has long term borrowing, means that the company has taken that from the market
(mainly banks).
It is very important for the
shareholders to keep a note of how high is the long term borrowings of the
company as compared to its equity.
Deferred tax liability is a
provisional fund maintained by the company using which they will pay the
forthcoming additional tax dues.
Has a part of non current liability
the company also hello kids some funds in the name of long term provisions.
Here the company keeps some cash reserves for paying their employees. These
payments can be like gratuity, provident funds, leave encashment. The
provisions can also be made for income tax payment, payment of dividend to
shareholders, dividend distribution tax etc.
Current liabilities
Current liabilities are those
obligation of the company that they must meet before 12 months.
If you will look into balance sheet
of any company in moneycontrol.com you will find four line items under the
heading current liabilities. They are, short term borrowing, trade payables,
other current liability and short term provisions.
Short term borrowing is essentially
that loan that company has taken from Bank CTC to fund there day-to-day cash
flow requirement. In financial term this is also called as working capital of
the company.
Trade payable is that money that a
company must pay to its suppliers within next 12 months.
Short term provisions are again
similar to long term provisions. The only difference here he is, this
provisions me get used within next 12 months.
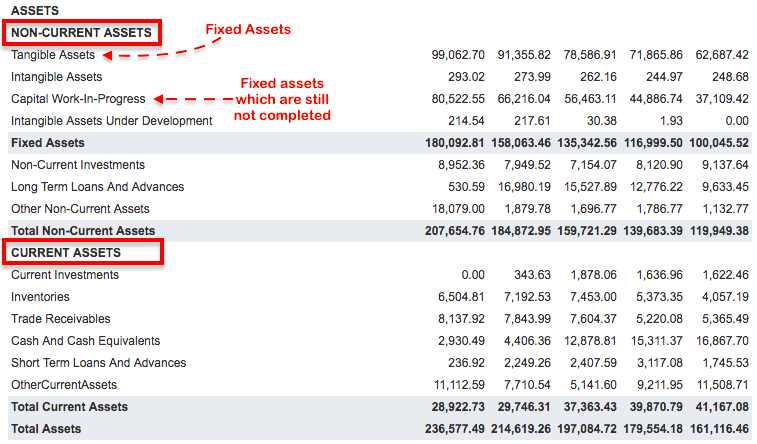
Assets
Generally in the balance sheet,
assets are categorised into two main types: non-current assets and current
assets.
Non-current assets are basically
property, plant, and equipment’s of the company. Normal terms we call it as
fixed assets of the company (Tangible assets).
Fixed Assets (Tangible Assets)
Fixed assets adults assets of the
company which they use directly for the production of goods and services for
their customers.
Common examples of fixed assets are
land, factory buildings, machines, furniture’s, Motor vehicles etc.
Fixed assets are those assets of the
company which company gathers to hold them for long-term.
Contrast to the fixed assets, an
inventory is also an asset of the company. But company maintains the inventory
with the objective of selling them in near future.
Intangible assets
Assets of the company do not have a
physical substance. You cannot physically see it and touch it. Example off in
tangible assets can be like copyrights, trademarks, patents etc gathered
by the company over a period of time.
Capital work in progress
These are those assets which were
not ready at the time of preparation of the balance sheet. These are those
assets which are still not ready to produce goods and services for the company.
Hence, call costs that has gone into
the preparation of that as it is shown as capital work in progress off the
companies balance sheet.
Just to understand, let’s take a
small example. Pause cement manufacturing plant is putting up a new facility to
manufacture a new brand of cement. Average it may take 3 years for the company
to start production from this new facility. But the company will start spending
money on this asset from the first months itself. So, the cost that was into
the preparation of the new cement plant will be booked as capital work in
progress for the next three years.
As soon as the new plant will begin
production, all capital work in progress associated with this new plant will be
transferred as tangible asset.
Non-current investments
Current investments are those
investments made by the company which day would like to hold for more then next
12 months. Example of such an investment can be stockholding of another
company.
Generally current investments are
reported in the balance sheet equivalent to the market valuation of the
investment.
Current assets
Current assets are those assets of
the company which is expected to be converted into cash within next one year.
It is the current assets of the
company that helps them to maintain enough liquidity.
Current assets of the company helps
in management of the current liabilities.
One of the most reliable firms of
current assets cash and cash equivalent, inventory, it’s investments, account
receivables from its customers, and loans and advances given to associates/
suppliers. Advances are also referred to as pre-paid expenses in some balance
sheets.
To
Conclude
You can see the above snapshot of a
typical balance sheet of a company and understand what is actually balanced in
a balance sheet.
Total asset of a business is always
equal to the sum of its total liability and shareholders funds.
How
balance sheet is related with its profit and loss accounts?
Reserves & Surplus in balance sheet gets updates every time the company makes
net profit (PAT). Net profit appears in companies profit and loss
accounts.
Debt (long term and short term borrowings) in balance sheet
increases the companies Finance cost which appears in companies profit
and loss accounts.
Trade payables of the balance sheet is a portion of expense to be
incurred by the company in the next financial year (FY). Companies often buy goods
and services from the suppliers on credit. All expenses which are booked by the
company appears in the profit and loss accounts.
Tangible assets valuation appearing
in balance sheet are recorded as net of accumulated depreciation (over last
several years of operation). Depreciation applicable only for a particular FY,
appears in the companies profit and loss accounts.
Non-current and current investments made by the company is recorded in companies balance sheet.
The income generated by these investments are recorded as other income
in profit and loss accounts.
Trade receivables appearing in
balance sheet of the company is the out of sales revenue. Companies often sell
their products and services to their customers on credit. This credit payment
due, to be paid by next months are recorded as trade receivable.
So now you can understand well, how
balance sheet and profit and loss accounts communicate with each other.
Disclaimer: All blog posts of
https://nse-bse-mcx-technicalanalysis.blogspot.com/ are for
information only. No blog posts should be considered as an investment
advice or as a recommendation. The user must self-analyze all securities
before investing in one.